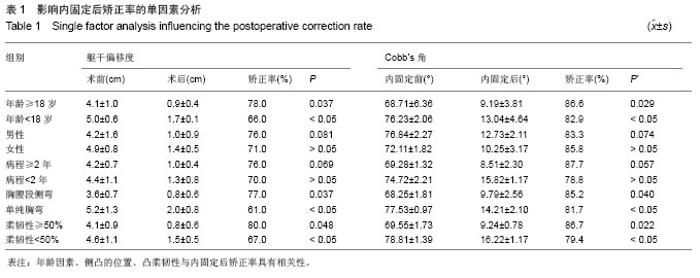
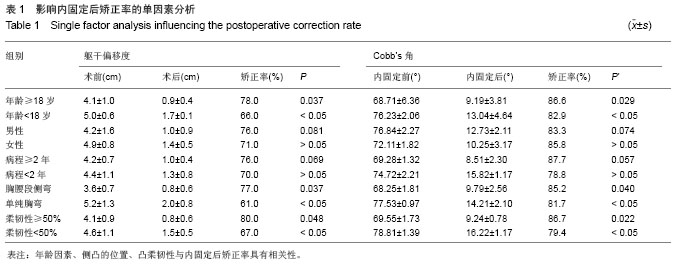
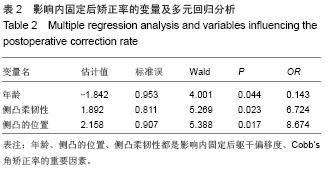
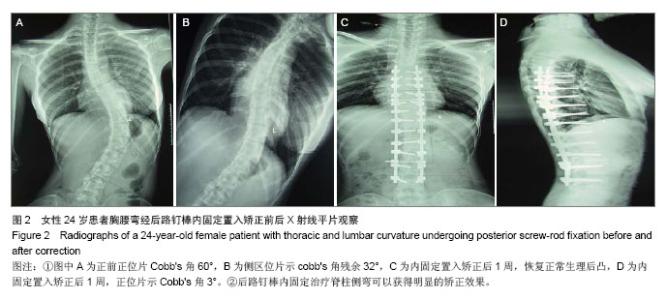
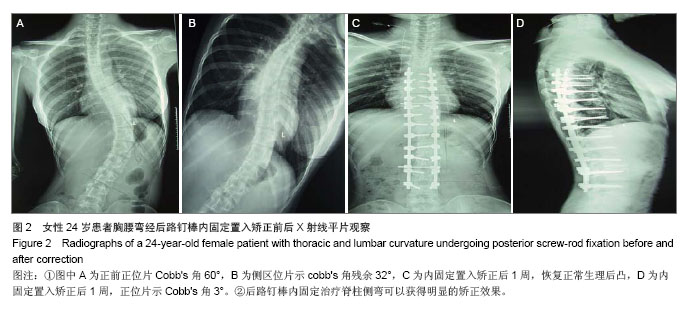
| [1]覃佳强,张德文.儿童脊柱畸形的支具治疗[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2004,12(1):25-27.[2]Bradford DS,Tay BK,Hu SS. Adult scoliosis:surgical indications,operative management,complications,and outcomes. Spine. 1999;24(24):2617-2629.[3]Harrington PR. Treatment of scoliosis. Correction and internal fixation by spine instrumentation.J Bone Joint Surg Am.1962 (44-A):591-610.[4]Smith JA. Adult deformity:management of sagittal plane deformity in revision adult spine surgery. Orthopaedics. 2001; 12(3):206-215.[5]Luque ER. The anatomic basis and development of segmental spinal instrumentation.Spine. 1982;7(3):256-259.[6]Buttermann GR, Thorson TM, Mullin WJ. Outcomes of posterior facet versus pedicle screw fixation of circumferential fusion: a cohort study. Eur Spine J. 2013 Oct 2. [7]Cotrel Y,Duhousset J. A new technic for segmental spinal osteosynthesis using the posterior approach.Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 1984;70(6):489-494.[8]Kim YJ,Lenke LG,Cho SK.et al. Comparative analysis of pedicle screw versus hook instrumentation in posterior spinal fusion of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 2004;29(18): 2040-2048.[9]邱贵兴,庄乾.青少年特发性脊柱侧凸的流行病学研究进展[J].中华医学杂志,2006,86(11):790.[10]Robert F.Heary ,Todd J.Albert.Spinal Deformities[M].New York,USA:Thieme Medical Publishers,2007:2-3. [11]周春光,刘立岷,宋跃明,等.重度僵硬性特发性脊柱侧凸患者术后肺功能变化[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2010,24(1):23-26.[12]Ni H, Zhu X, He S, et al. An increased kyphosis of the thoracolumbar junction is correlated to more axial vertebral rotation in thoracolumbar/lumbar adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(23):E1334-1338. [13]王智伟,邱勇,王渭君,等.青少年特发性主胸弯脊柱侧弯患者骨盆旋转的影响因素[J].中华小儿外科杂志,2012,33(2): 126-130.[14]Lenke LG, Sides BA, Koester LA, et al.Vertebral column resection for the treatment of severe spinal deformity. Clin Orthop RelatRes. 2010;468(3):687-699.[15]刘巍,陈庆贺.青少年特发性脊柱侧凸的手术治疗[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010,16(5):405-408.[16]Sarlak AY, Bulu L, Sarisoy HT, et al. Placement of pedicle screws in thoracic idiopathic scoliosis: a magnetic resonance imaging analysis of screw placement relative to structures at risk.Eur Spine J.2008;17(5):657.[17]Wang X, Pang X, Wu P, et al. One-stage anterior debridement, bone grafting and posterior instrumentation vs. single posterior debridement, bone grafting, and instrumentation for the treatment of thoracic and lumbar spinal tuberculosis. Eur Spine J. 2013 Oct 1. [18]Popp AW, Schwyn R, Schiuma D, et al. DensiProbe Spine: an intraoperative measurement of bone quality in spinal instrumentation. A clinical feasibility study. Spine J. 2013; 13(10):1223-1229. [19]Pizanis A, Holstein JH, Vossen F, et al. Compression and contact area of anterior strut grafts in spinal instrumentation: a biomechanical study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013;14: 254. [20]Cho W, Mason JR, Smith JS, et al. Failure of lumbopelvic fixation after long construct fusions in patients with adult spinal deformity: clinical and radiographic risk factors: clinical article. J Neurosurg Spine. 2013;19(4):445-453. [21]Choi KC, Ryu KS, Lee SH, et al. Biomechanical comparison of anterior lumbar interbody fusion: stand-alone interbody cage versus interbody cage with pedicle screw fixation -- a finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013;14: 220. [22]Shapiro GS,Taira G,Boachie-Adjei O. Results of surgical treatment of adult idiopathic scoliosis with low back pain and spinal stenosis:a study of long-term clinical radiographic outcomes. Spine 2003;28(4):358-363.[23]Wu P, Luo C, Pang X, et al. Surgical treatment of thoracic spinal tuberculosis with adjacent segments lesion via one-stage transpedicular debridement, posterior instrumentation and combined interbody and posterior fusion, a clinical study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;133(10): 1341-1350. [24]Suk SI, Kim JH, Kim SS, et al. Thoracoplasty in thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2008; 33(10):1061-1067. |